In this article, we will be learning about Positions. So let get's started. Let's first understand the position.
What is Position?
The position is the property in the CSS which is used to set or position the HTML element. We can position the element wherever we want as per the need.
There are 5 types of Positions:
- Static
- relative
- Absolute
- fixed
- sticky
Let's get started with the static Position
1. Static
- Static is the default position that every HTML element have.
- You do not need to add anything to your code
- Static is the by-Default behavior of every HTML tag
2. Relative
- Relative is the most used position in CSS
- As a Developer, you will be using this position a lot
- Let's understand it with code example
<body>
<div class="relativePosition"></div>
</body>
<style>
.relativePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
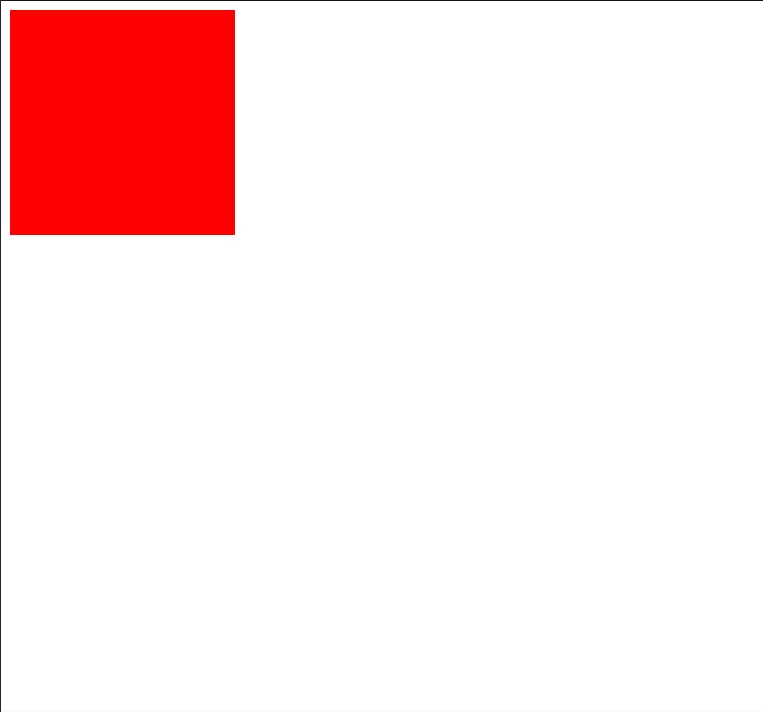
Img-2.1
- In the above code example I have just created a div and gave a background color to it
- By-Default its position is Static
- Now we need to change the position to relative
- When we change the position to relative we also need to mention 4 new properties:
- (Right, Left, top, Bottom)
<body>
<div class="relativePosition"></div>
</body>
<style>
.relativePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
top: 80px;
left: 150px;
}
</style>
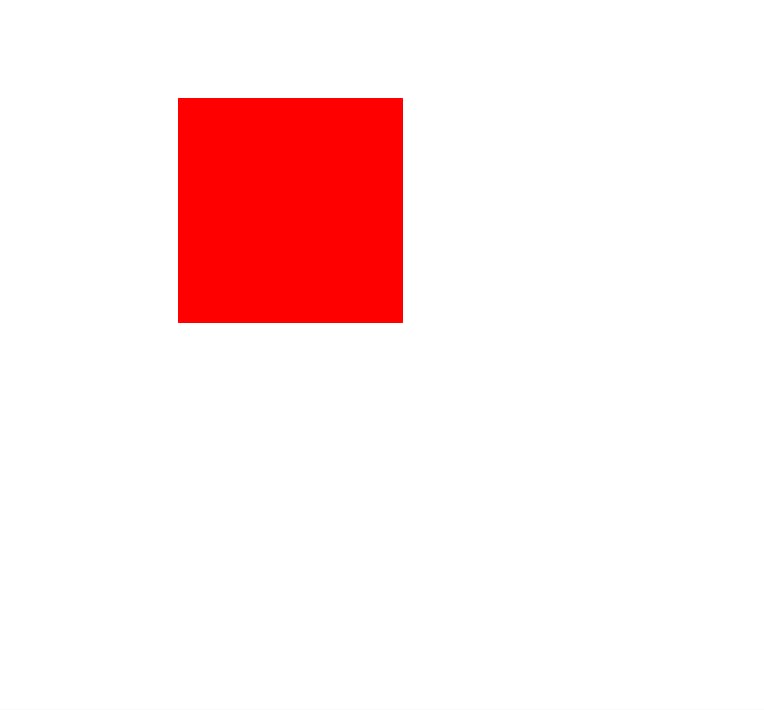
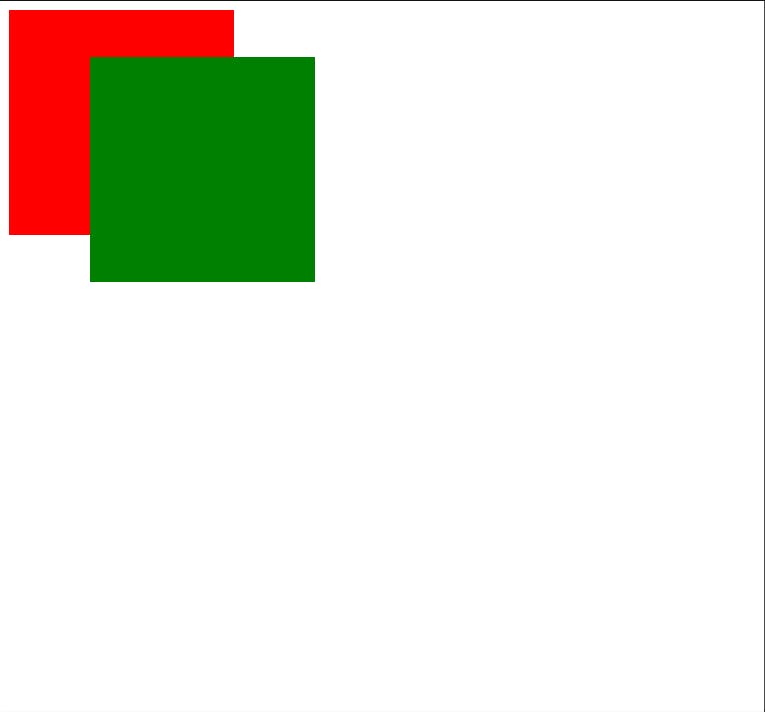
Img-2.2
- Here you can see that the red box position changed drastically.
Let's understand how this happened.
- Relative Position takes reference from its original position.
- where was my red box earlier?
- Now from that position move my box
80px from topand150px from left - You can check the result in the image-2.1 and image-2.2
- In image-2.2 red box is
80 px down from it's original position`150px left from its original position
So, Relative Position takes reference from its original position and moves from its existing position
3. Absolute
- Absolute is the most confusing position in CSS
- It is mainly used when we work with images
- As a Developer, you will be using this position a lot, so you need to master it
- Let's understand it with code example
<body>
<div class="relativePosition"></div>
<div class="absolutePosition"></div>
</body>
.relativePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.absolutePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
}
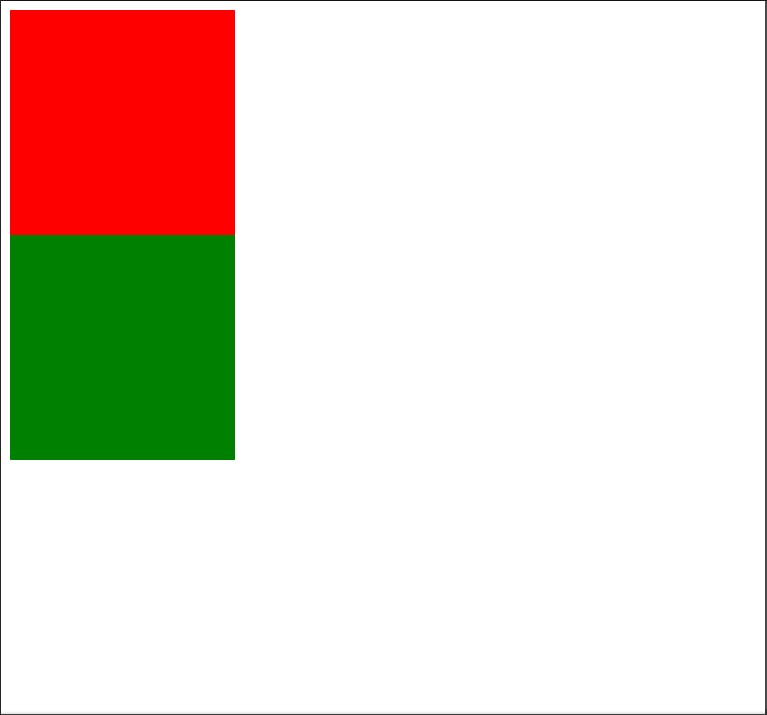
Img- 3. 1
- In the above code we have just created a div and gave it a background color of green.
- Now Let's understand about Position Absolute
- For that, we need to add the position Absolute, with 4 properties (i.e right, left, top, bottom)
<body>
<div class="relativePosition"></div>
<div class="absolutePosition"></div>
</body>
<style>
.relativePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.absolutePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 80px;
}
</style>
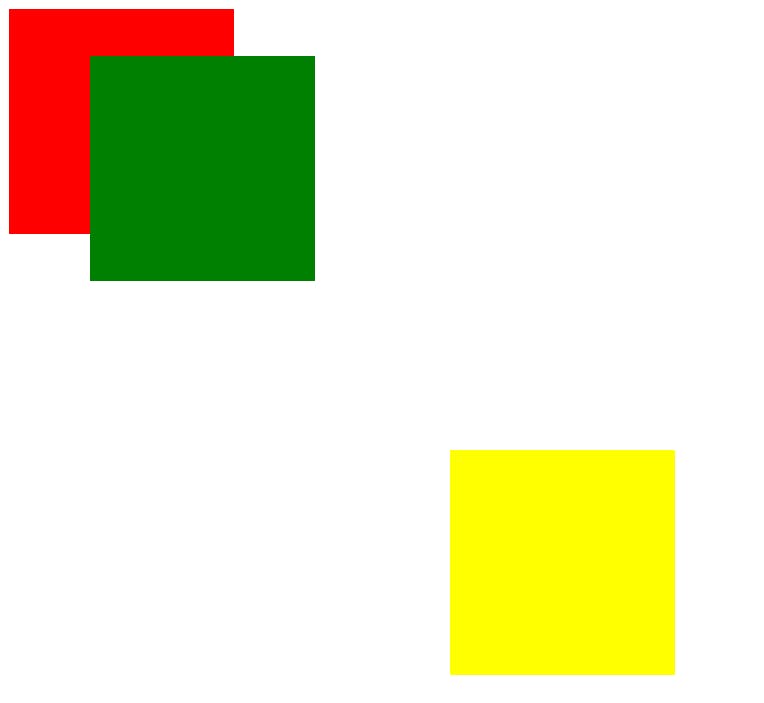
Img-3. 2
- Here you can see that the green box position changed drastically.
Let's understand how this happened.
- Absolute Position takes reference from its
neighboring element or parent element - Its Earlier or Original position
Does not Matteras in the case of Relative - Absolute does not care about the element Original Position
- Move my green box
50px down from the Parent Element Topand80px towards left from parent element - You can check the result in the image-3.1 and image-3.2
- In image-3.2 green box is
50 px down from it's parent position`150px left from its parent position
So, Absolute Position takes reference from its parent's position and moves according to its parent's position
4. Fixed
- Fixed is another type of position in CSS
It is mainly used when we need to fix the position of an element
Let's understand it with code example
<body>
<div class="relativePosition"></div>
<div class="absolutePosition"></div>
<div class="fixedPosition"></div>
</body>
<style>
.relativePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.absolutePosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 80px;
}
.fixedPosition {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
position: fixed;
top: 400px;
left: 400px;
}
</style>
Img-4. 1
- Here you can see that we have created a new div with a background color of yellow
- Fixed Position takes reference from
Window Object i.e Browser - Its Earlier or Original position
Does not Matteras in the case of relative - Its Parent/neighboring position also
DOES NOT MATTERas in the case of absolute - Move my yellow box
400px down from the top of the browserand400px towards left from browser - You can check the result in the image-4.1
- In the image-4.1 yellow box is
400 px down from the browserand400px left from the browser
So, Fixed Position takes reference from its browser window and moves according to the browser window
5. Sticky
- Sticky is another type of position in CSS
It is mainly used with the Navigation bar, when we scroll down we want your content to stick at the top
Let's understand it with code example
<body>
<nav>
<ul class="stickyPosition">
<li>Home</li>
<li>About</li>
<li>Contact</li>
</ul>
</body>
<style>
.stickyPosition {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
background-color: gold;
}
.largerarea {
background-color: lightcyan;
height: 150vh;
}
</style>
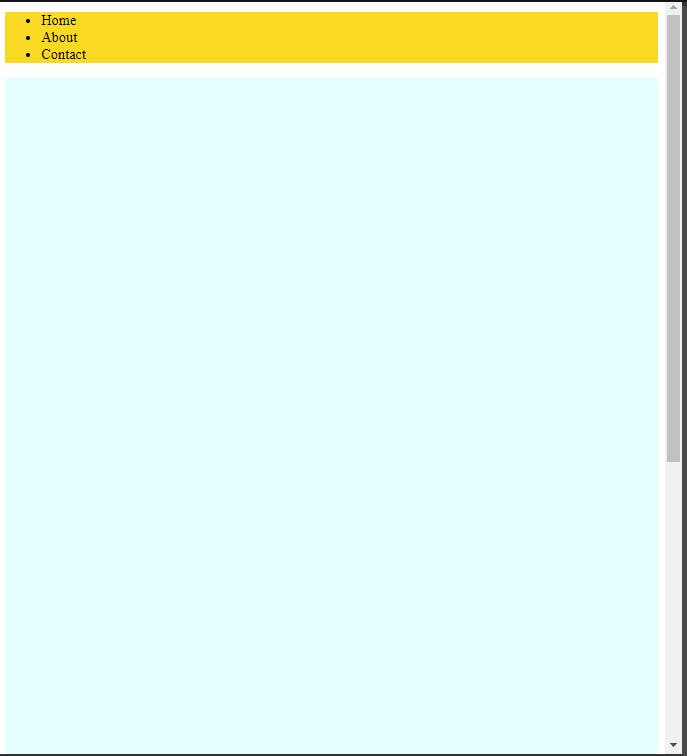
Img-5. 1
- In the above code you can see that we have a navigation list and a div tag with a height of 150vh so that we can scroll down
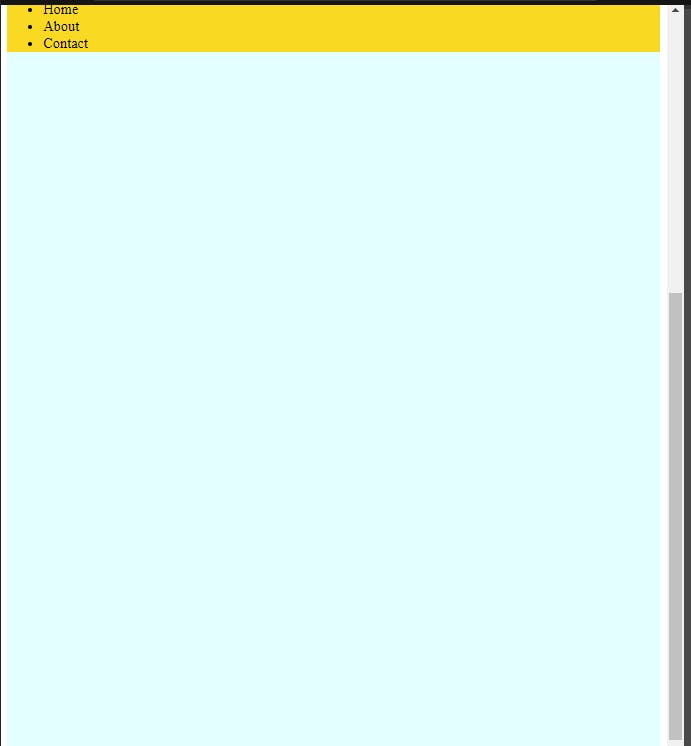
Img-5. 2
- You can check the result in the image-5.1 and 5.2
- When we scroll down, the list got stuck at the top with help of position sticky
The Crunch of Entire Article
`Relative Takes reference from its original position`
`Absolute Takes reference from its parent`
`Fixed takes reference from browser`
`Sticky got fixed at the top`
`Static is by Default behavior`
Thanks!!